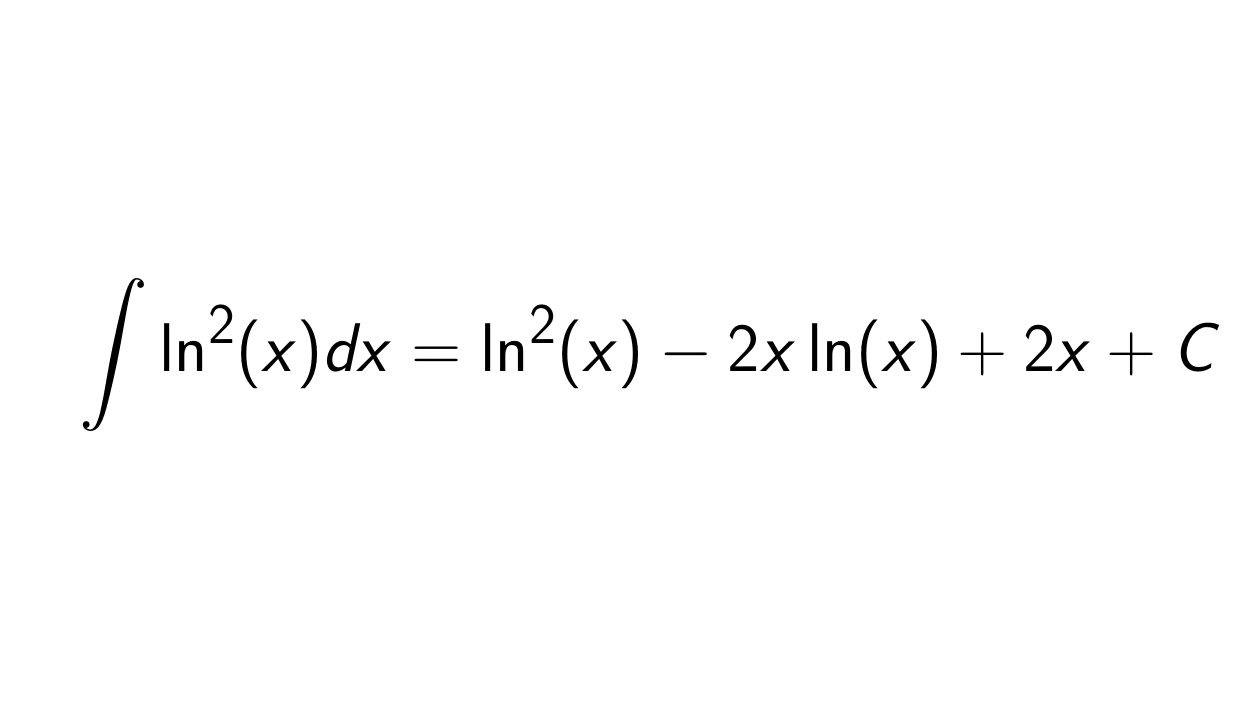Solution. We want to determine the integral of \ln^2(x), i.e.:
\begin{align*}
\int \ln^2(x) dx.
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
\int U dV = UV - \int VdU,
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
\int \ln^2(x) dx &= \ln^2(x)\cdot x - \int x \cdot \frac{2\ln(x)}{x}dx \\
&= x\ln^2(x) - \int 2\ln(x) dx.
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
\int \ln^2(x) dx &= x\ln^2(x) - \int 2\ln(x) dx \\
&= x\ln^2(x) - (2x\ln(x) - \int \frac{2x}{x} dx )\\
&= x\ln^2(x) - 2x\ln(x) + \int 2 dx \\
&= x\ln^2(x) - 2x\ln(x) + 2x + C.
\end{align*}