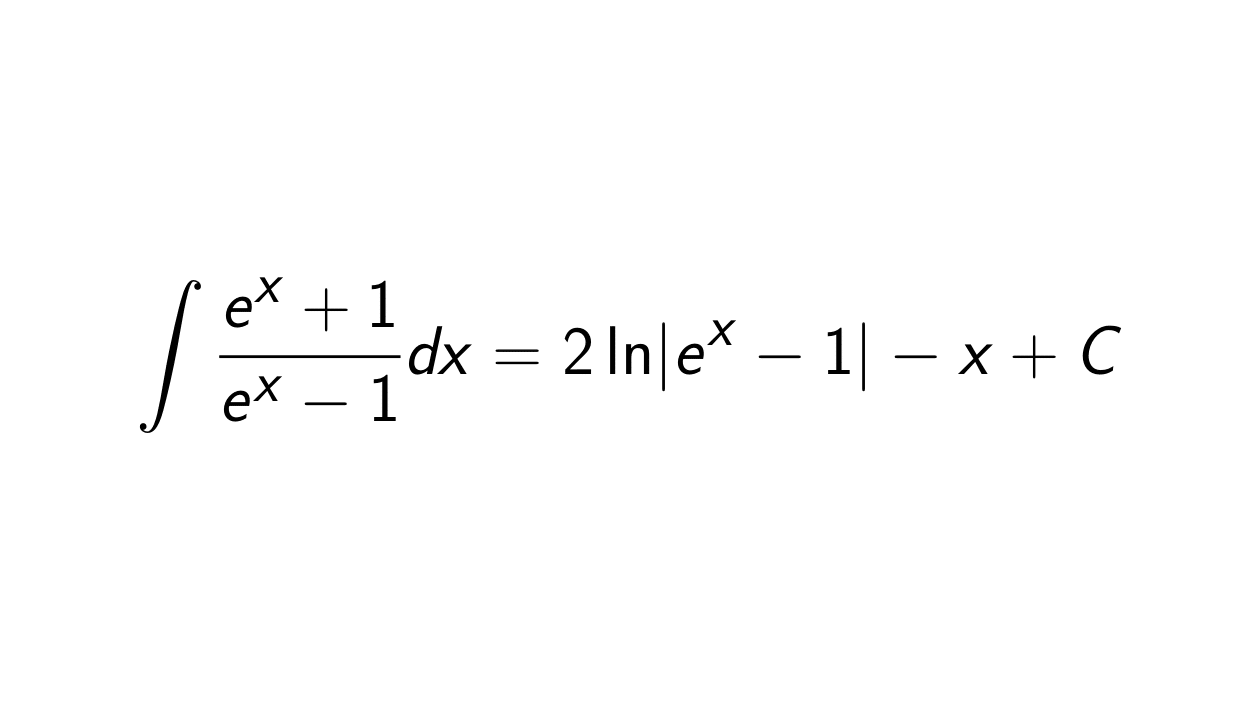Solution. We want to determine the integral of \frac{e^x + 1}{e^x - 1}, i.e.:
\begin{align*}
\int \frac{e^x + 1}{e^x - 1} dx = \int \frac{e^x}{e^x - 1} dx + \int \frac{1}{e^x - 1} dx.
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
\int \frac{e^x}{e^x - 1} dx &= \int \frac{du}{u} \\
&= \ln \lvert u \rvert + C_1 \\
&= \ln \lvert e^x - 1 \rvert + C_1,
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
\int \frac{1}{e^x - 1} dx = \int \frac{1}{e^x(1 - e^{-x})} dx = \int \frac{e^{-x}}{1 - e^{-x}} dx.
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
\int \frac{e^{-x}}{1 - e^{-x}} dx &= \int \frac{dv}{v} \\
&= \ln \lvert v \rvert + C_2 \\
&= \ln \lvert 1 - e^{-x} \rvert + C_2 \\
&= \ln \lvert e^{-x}(e^x - 1) \rvert + C_2 \\
&= \ln \lvert e^{-x} \rvert + \lvert e^{-x} - 1 \rvert + C_2 \\
&= -x + \lvert e^{-x} - 1 \rvert + C_2,
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
\int \frac{e^x + 1}{e^x - 1} dx &= \int \frac{e^x}{e^x - 1} dx + \int \frac{1}{e^x - 1} dx \\
&= \ln \lvert e^x - 1 \rvert + C_1 -x + \lvert e^{-x} - 1 \rvert + C_2 \\
&= 2\ln\lvert e^x - 1 \rvert - x + C,
\end{align*}