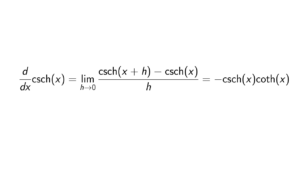
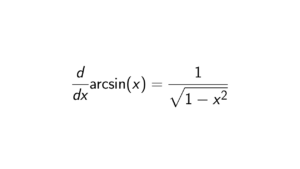Solution. Let f(x) = \cosh(x). We know by the definition of \cosh(x) that
\begin{align*}
\cosh(x) = \frac{e^x + e^{-x}}{2}.
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
f'(x) &= \frac{d}{dx} \cosh(x) \\
&= \frac{d}{dx} \frac{e^x + e^{-x}}{2} \\
&= \frac{d}{dx} \frac{e^x}{2} + \frac{d}{dx} \frac{e^{-x}}{2} \\
&= \frac{e^x}{2} + \frac{-e^{-x}}{2} \\
&= \frac{e^x}{2} - \frac{e^{-x}}{2} \\
&= \frac{e^x - e^{-x}}{2} \\
&= \sinh(x).
\end{align*}