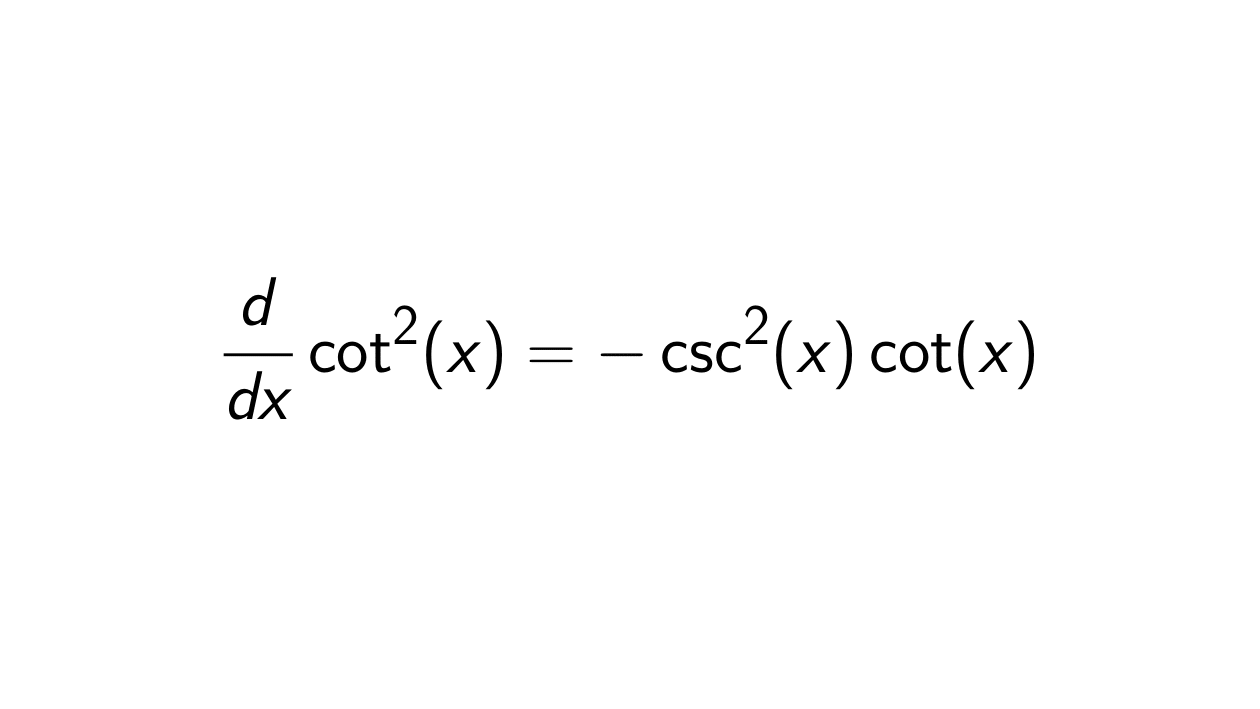Solution. Let F(x) = \cot^2(x), f(u) = u^2, and g(x) = \cot(x) such that F(x) = f(g(x)). We will use the chain rule to determine the derivative of \cot^2(x):
\begin{align*}
F'(x) = f'(g(x))g'(x).
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
f'(g(x)) = 2g(x) = 2\cot(x) \quad \text{and} \quad g'(x) = -\csc^2(x).
\end{align*}\begin{align*}
F'(x) &= f'(g(x))g'(x) \\
&= 2\cot(x)\cdot(-\csc^2(x)) \\
&= -2\cot(x)\csc^2(x).
\end{align*}